What is an anal fissure?
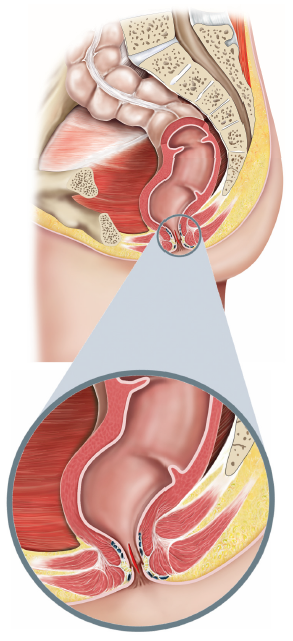
An anal fissure is a tear in the skin around your back passage (see figure 1). It is a common problem that causes severe pain, especially after a bowel movement. It may also cause bleeding.The condition is associated with spasm of the internal anal sphincter. This reduces the blood supply to the area and prevents healing. The treatment is aimed at breaking this cycle to allow healing to take place.
What are the benefits of surgery?
Surgery should help the anal fissure to heal but is usually recommended if the fissure has not healed with non-surgical treatments.
Are there any alternatives to surgery?
There are simple treatments which may help such as laxatives, ointments, injections of Botox, increasing the amount of fibre in your diet and drinking plenty of fluid.
What does the operation involve?
Sphincterotomy simply means dividing the sphincter. The operation is usually performed under a general anaesthetic and takes about 15 minutes.Your surgeon will make a small cut on the skin near your back passage. They will cut the lower part of the internal sphincter muscle. This will relieve the spasm in the sphincter, allowing a better blood supply to heal the fissure.
What complications can happen?
1. General complications
- Pain
- Bleeding
- Infection of the surgical site (wound)
2. Specific complications
- Involuntarily passing wind or loose faeces
- Difficulty passing urine
- Permanent incontinence from your bowel
How soon will I recover?
You should be able to go home the same day.
The pain from the fissure should improve rapidly. You should be able to return to work after a few days, depending on your type of work. Regular exercise should help you to return to normal activities as soon as possible. Before you start exercising, ask the healthcare team or your GP for advice.
Acknowledgments
Author: Mr Jonathan Lund DM FRCS (Gen. Surg.), Illustrations: Medical Illustration Copyright © Medical-Artist.com
This document is intended for information purposes only and should not replace advice that your relevant health professional would give you.